Hydraulic Modelling
The use of mathematical models within GIS to simulate water flowthrough natural or built environments, critical for flood risk, drainage, and hydrological studies.
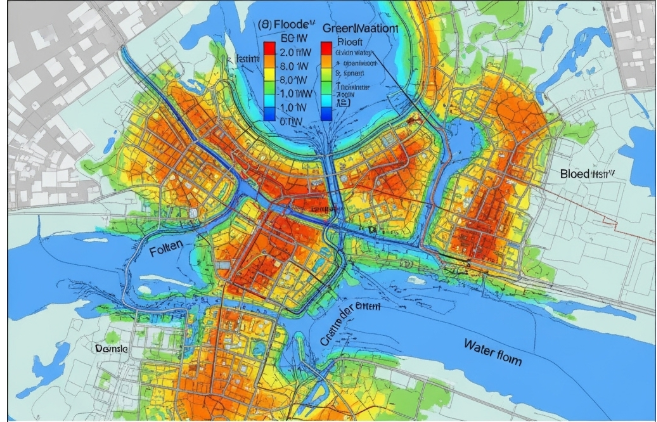
How do you define a Hydraulic Modelling?
Hydraulic modelling is the process of simulating the behaviour and movement of fluids, mainly water, in natural or artificial systems using mathematical and computational methods. It aids in forecasting the flow of water via drainage systems, pipes, channels, and rivers under different circumstances.
Among the main goals of hydraulic modelling are:
Examining water levels and flood threats
Creating sewage and water supply systems
Controlling runoff from stormwater
Analysing how infrastructure projects affect water flow
Depending on how complex the system under study is, hydraulic models can be one-, two-, or three-dimensional. In order to make well-informed decisions on water resources, they are crucial instruments in the fields of civil engineering, environmental management, and urban planning.
Related Keywords
The flow of water via systems including rivers, stormwater networks, water supply pipes, and wastewater systems can be simulated and examined using hydraulic modelling software. With the aid of these technologies, engineers can better distribute water, forecast flooding, design effective infrastructure, and evaluate system performance in a variety of situations. EPANET, HEC-RAS, InfoWorks, and Mike Hydro are well-known solutions.
In order to forecast flood behaviour under different circumstances, flood risk hydraulic modelling simulates water flow in rivers, streams, and urban drainage systems. It assists in identifying places that are susceptible to flooding, estimating flood depths, and informing mitigation plans by examining variables such as rainfall, geography, river capacity, and land use. Planning for disasters, designing infrastructure, and maintaining community safety all depend on this modelling.
The technique of utilizing computer tools to simulate the flow, velocity, and behaviour of water in rivers and streams is known as river hydraulic modelling. It aids environmental scientists and engineers in understanding sediment motion, designing hydraulic structures, maximizing water resources, and assessing flood risks. Hydraulic models accurately estimate water levels and flow patterns under various conditions by combining topography, hydrological inputs, and field data.
While validation checks the model against independent data to guarantee precise and trustworthy forecasts for water systems, hydraulic model calibration modifies parameters to fit observed flow data.
