Ring Buffer
A spatial analysis technique that creates multiple concentric buffer zones around a feature, useful for distance-based impact studies (inferred from standard GIS usage).
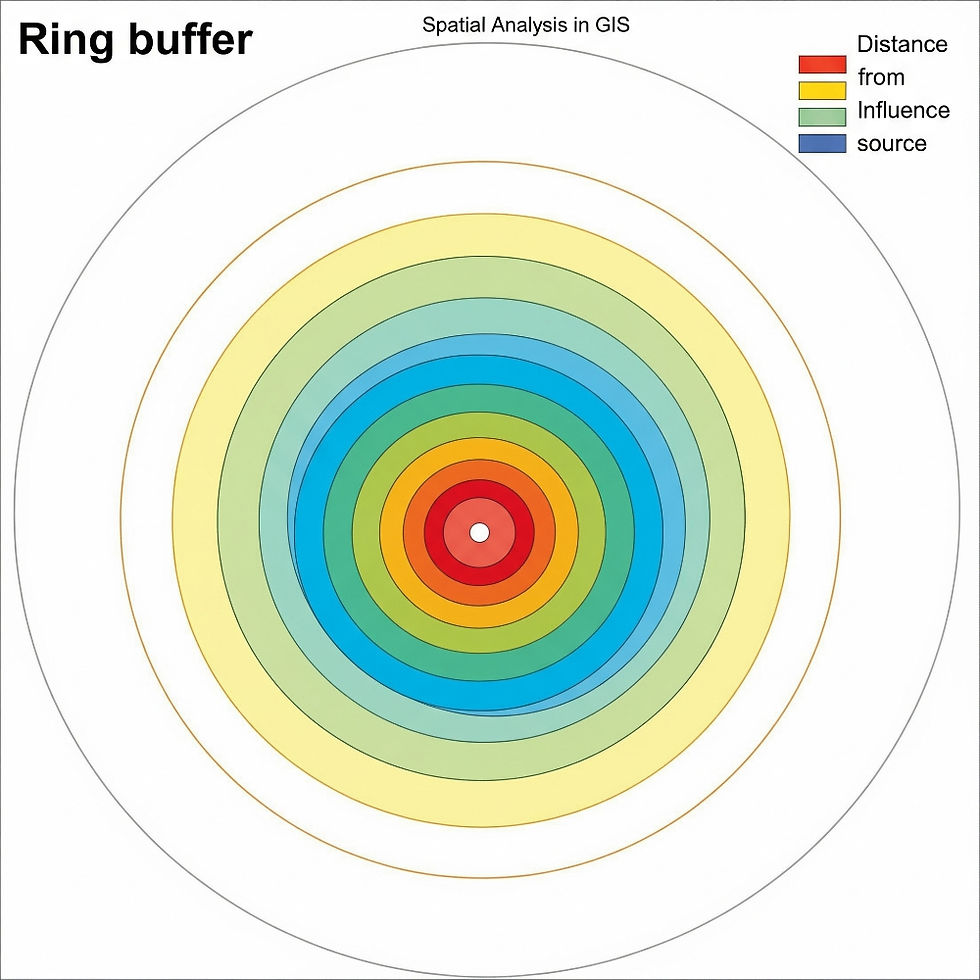
What is Ring Buffer?
In GIS, a ring buffer is a geographic analysis method that surrounds a point, line, or polygon feature with several concentric buffer zones. Several zones that can be used for in-depth proximity analysis are formed by each ring, which indicates a distinct distance from the feature.
Important Features:
Zones of Concentration: At equal or predetermined intervals, such as 0–1 km, 1–2 km, and 2–3 km, rings are formed.
Non-overlapping: Ring buffers produce distinct zones that do not overlap, in contrast to conventional buffers.
Used For: Examining pollutant dispersion, service area coverage, or population distribution surrounding a facility, among other geographical effect or impact analyses at different distances.
Example Use Case: To determine service accessibility, a planner may divide the region into 1 km rings and use a ring buffer to determine how far away various towns are from a hospital.
Essentially, a Ring Buffer aids in the visualization and measurement of spatial interactions between various distance zones from a source feature.
Related Keywords
A ring buffer (circular buffer) is a fixed-size data structure whose data wraps around as it reaches the end, making it efficient for continuous data streams like music or networking.
A fixed-size data structure known as a circular buffer (or ring buffer) employs a single, continuous block of memory as though it were connected end-to-end. It effectively uses First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data management, automatically wrapping around when the buffer's end is reached. This makes it perfect for real-time processing, data streaming, and scenarios requiring constant-time operations and memory efficiency.
A ring buffer, also known as a circular buffer, is a fixed-size queue that, when full, replaces previous data.
class RingBuffer:
def __init__(self, size):
self.buffer, self.size, self.index = [None]*size, size, 0
def append(self, item):
self.buffer[self.index] = item
self.index = (self.index + 1) % self.size
def get(self):
return self.buffer
rb = RingBuffer(5)
for i in range(7): rb.append(i)
print(rb.get()) # [5, 6, 2, 3, 4]
In embedded systems, a circular data structure that recycles a fixed memory block is called a ring buffer. The oldest data is overwritten by new data once it is full. For effective data handling in real-time operations like UART communication, it is frequently utilized.
