Spatial Modelling
Analytical procedures and methodologies used to derive information about spatial relationships between geographic phenomena.
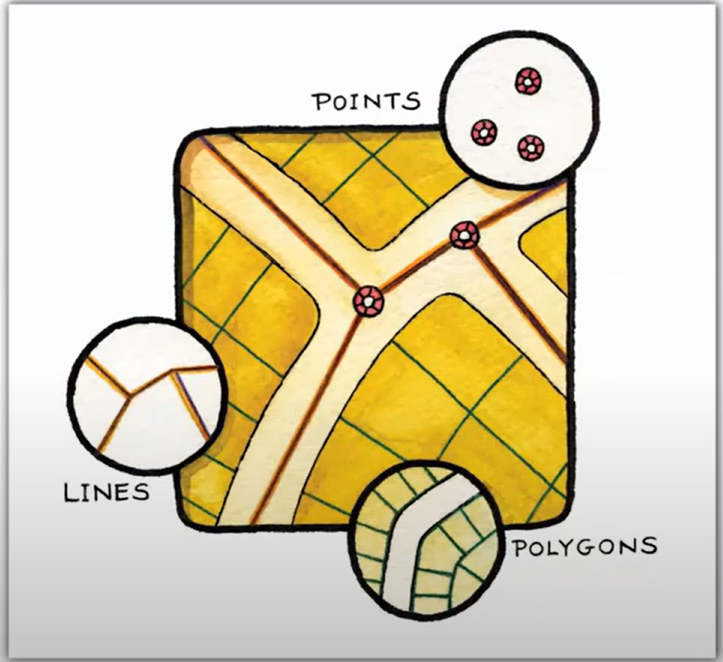
What does the term Spatial Modelling mean?
In GIS, "spatial modelling" refers to the process of representing, analysing, and simulating real-world spatial phenomena using mathematical and computational models. Illustrating the relationships between objects in space and time, it aids in the comprehension of intricate geographic systems.
Definition: Spatial modelling is the process of examining geographic data to forecast results based on spatial correlations and replicate natural or man-made processes.
Planning for new urban development is an example of a use case.
Combine land use categories, elevation (to prevent slopes), distance from roadways, and flood risk using spatial modelling.
A suitability map highlighting the ideal sites for building is the result.
Related Keywords
Examining geographic data to find trends, correlations, and patterns is known as GIS spatial analysis. In order to address practical issues in urban planning, environmental management, transportation, and disaster response, it makes use of methods such as overlay, buffering, proximity analysis, and spatial statistics. Spatial analysis assists organizations in making data-driven, well-informed decisions by incorporating location-based data.
Spatial data is arranged into understandable structures using geospatial data modelling, which demonstrates the connections between features and attributes. It supports planning, aids in pattern analysis, and forecasts results.
Using techniques like kriging, IDW, and spatial regression, spatial prediction methods estimate values at unsampled places. They support the modelling of patterns for resource management, urban planning, and environmental monitoring applications.
In GIS, the methods used to examine and decipher the spatial distributions, connections, and patterns of geographic data are referred to as spatial statistics. By taking into account the position and configuration of features on the earth's surface, it aids in the identification of trends, clusters, and anomalies. These techniques are frequently employed to assist data-driven decision-making in domains such as environmental research, public health, urban planning, and criminal analysis.
